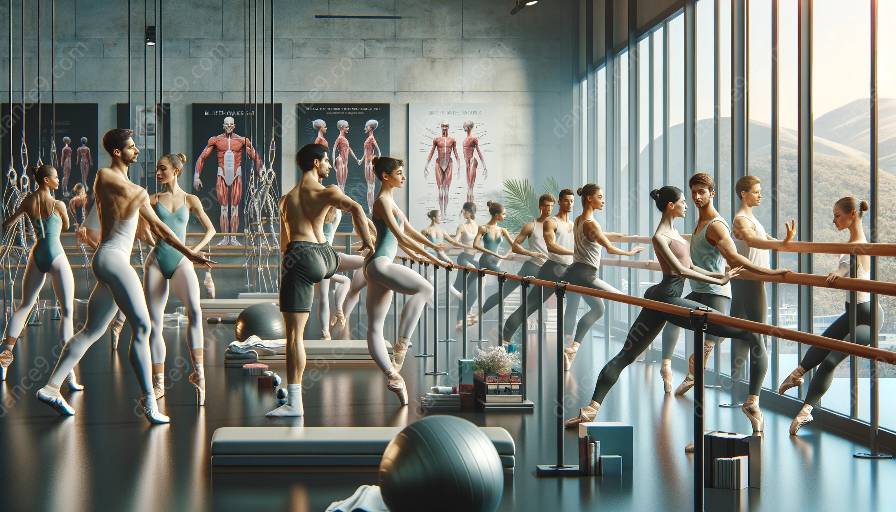
Ballet training provides a comprehensive approach to overall physical fitness, incorporating strength, flexibility, and endurance. Its health and physical aspects, as well as its historical and theoretical background, create a rich tapestry of benefits for the body and mind.
Health and Physical Aspects of Ballet
1. Strength: Ballet training involves various movements that target and strengthen specific muscle groups, particularly in the legs, core, and upper body. The emphasis on proper posture and alignment also helps develop overall strength and muscle tone.
2. Flexibility: Flexibility is a crucial component of ballet. Through regular stretching and exercises, dancers improve their range of motion, which contributes to joint health and overall flexibility.
3. Endurance: Ballet dancers require exceptional stamina to perform intricate and demanding routines. Training in ballet builds cardiovascular endurance and enhances overall physical stamina.
Ballet History and Theory
1. Historical Significance: Ballet has a rich history dating back to the Italian Renaissance courts. Over the centuries, it has evolved into a highly technical and expressive art form that continues to captivate audiences worldwide.
2. Technical Foundations: Ballet training is rooted in precise technique and form, which not only contributes to its aesthetic appeal but also provides a structured framework for physical development and discipline.
3. Artistic Expression: Beyond the physical aspects, ballet encompasses emotional and artistic expression. Dancers learn to convey narratives and emotions through their movements, enhancing their mental and emotional well-being.
In conclusion, ballet training offers a holistic approach to overall physical fitness, integrating health and physical aspects with a rich historical and theoretical context. Its multifaceted benefits make it a unique and compelling form of exercise for individuals seeking to enhance both their physical and mental well-being.