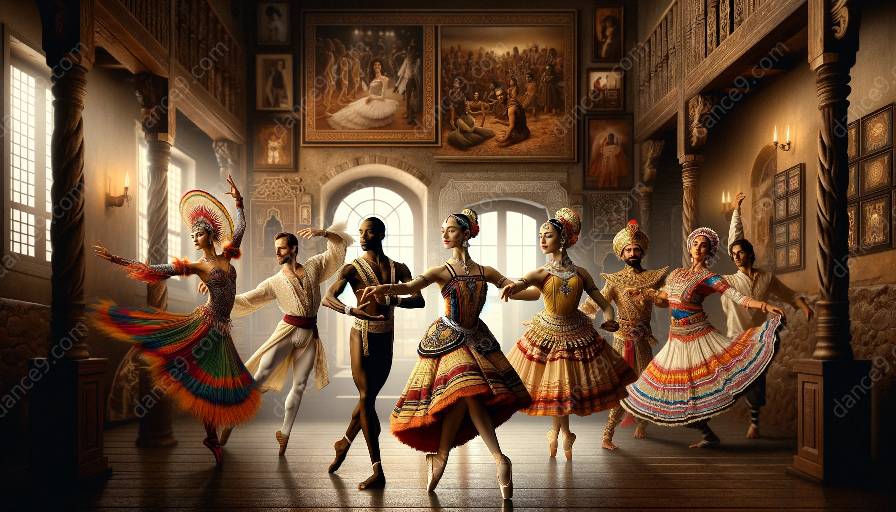
Traditional dance is deeply rooted in the cultural heritage of various communities around the world. It serves as an embodiment of history, customs, and social dynamics, reflecting the unique cultural context in which it originates. When delving into the understanding of traditional dance, it is essential to consider how the cultural context influences its interpretation. This exploration provides an insightful journey into dance ethnography and cultural studies.
The Significance of Tradition in Dance
Tradition plays a pivotal role in dance, serving as a vehicle for the preservation and transmission of cultural heritage. Traditional dances encapsulate the values, beliefs, and rituals of a community, offering a window into the collective identity of a particular group or society. The movements, gestures, and music in traditional dance hold profound meaning that is deeply intertwined with the cultural context in which they were developed.
Cultural Context and Interpretation
The interpretation of traditional dance is intricately linked to its cultural context. Culture influences every aspect of traditional dance, from its choreography and symbolism to its performance and social significance. The interpretation of traditional dance takes into account the historical, religious, and social elements of the culture in which it is situated. For example, a traditional dance from a society that values communal harmony might emphasize collective movements and group dynamics, while a dance from a culture that reveres individual expression may focus on solo performances and personal storytelling.
Regional Variations and Local Influences
Traditional dance is not homogenous across different cultures and regions. Each community's unique cultural context shapes the development and interpretation of its traditional dance forms. Regional variations and local influences result in diverse styles, movements, and thematic expressions within traditional dance. For instance, the traditional dance of a coastal community may reflect the influence of seafaring traditions and maritime culture, while a dance from an agricultural society might incorporate movements inspired by farming and harvest rituals.
Role of Dance Ethnography
Dance ethnography offers a comprehensive approach to studying the cultural context and interpretation of traditional dance. By immersing in the community where the dance originates, dance ethnographers gain valuable insights into the cultural, social, and historical factors that inform the dance form. Ethnographic research provides a deeper understanding of the symbolic meanings, ritualistic elements, and community dynamics associated with traditional dance, shedding light on how cultural context shapes its interpretation.
Impact of Globalization
Globalization has brought about significant changes in the interpretation and evolution of traditional dance. The influx of external influences, cross-cultural interactions, and modernization has impacted the traditional dance practices of many communities. As traditional dance encounters global audiences and contemporary trends, its interpretation and presentation may undergo adaptation and transformation, leading to new hybrid forms of cultural expression.
Cultural Studies and Traditional Dance
Cultural studies provide a multidisciplinary lens through which the influence of cultural context on the interpretation of traditional dance can be analyzed. This approach involves examining the historical, sociopolitical, and anthropological dimensions of traditional dance within its cultural context. By situating traditional dance within broader cultural frameworks, cultural studies reveal the interconnectedness of dance, identity, power dynamics, and social narratives, offering valuable perspectives on the diverse ways in which traditional dance reflects and shapes cultural identity.
Conclusion
The influence of cultural context on the interpretation of traditional dance is a dynamic and multifaceted phenomenon. It encompasses the rich tapestry of cultural traditions, rituals, social structures, and historical narratives that shape traditional dance forms. Understanding this influence is essential for fostering cross-cultural appreciation, preserving intangible cultural heritage, and engaging in meaningful dialogue about the complexities of human expression through dance.