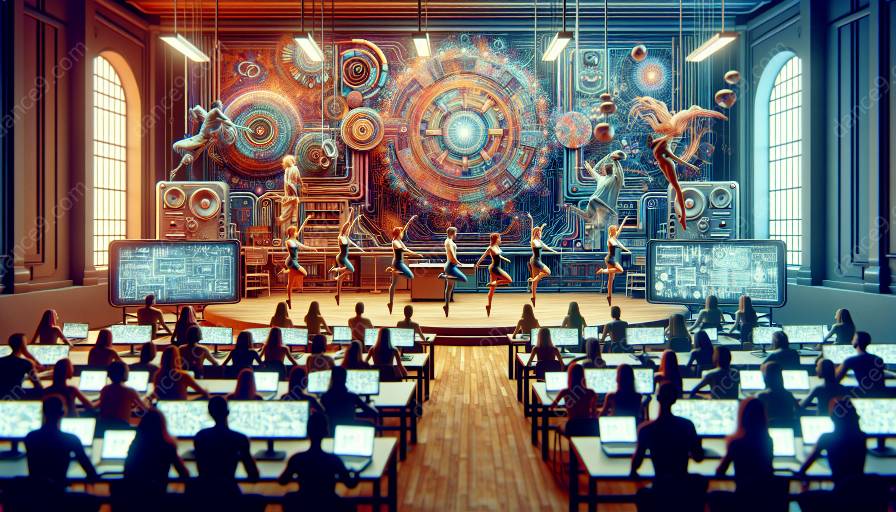
As technology continues to intersect with the performing arts, the integration of motion graphics in dance has become increasingly popular. The use of digital animations and visual effects enhances the visual appeal of dance performances, creating a multidimensional experience for both performers and audiences. However, incorporating motion graphics in dance also introduces unique safety considerations that performers and production teams must address to ensure a seamless and secure performance. This article explores the safety considerations involved in merging motion graphics with dance, providing insights into the technical, artistic, and ergonomic aspects of this collaboration.
The Intersection of Dance and Technology
In recent years, the intersection of dance and technology has led to innovative collaborations that push the boundaries of traditional performance art. Motion graphics, which involve the visual representation of motion through digital animation, offer dancers and choreographers a new canvas for creative expression. By seamlessly integrating visual effects with live dance performances, artists can transport audiences into immersive and dynamic worlds, blurring the lines between reality and virtuality.
Incorporating Motion Graphics in Dance Performances
The incorporation of motion graphics in dance performances requires a meticulous fusion of choreography, technology, and stage design. The process often begins with conceptualizing the visual narrative that will complement the dance piece, followed by the creation of digital assets such as 3D models, motion-capture data, and visual effects. These elements are then seamlessly blended with live-action performances through projection mapping, LED screens, or holographic displays, enhancing the overall visual impact of the choreography.
Safety Considerations for Performers and Crew
When implementing motion graphics in dance performances, several safety considerations must be taken into account to protect the well-being of performers and production crew:
- Integration of Technology: The seamless integration of motion graphics with live dance requires meticulous attention to technical details. Performers must be trained to navigate digital environments and interact with projected or virtual elements without compromising their physical safety.
- Ergonomic Design: Stage design plays a crucial role in ensuring the ergonomic integration of motion graphics. Projection surfaces, LED screens, or holographic displays must be strategically positioned to provide optimal visibility and interaction for performers, minimizing the risk of collisions or compromised movement.
- Technical Rehearsals and Protocols: Prior to live performances, extensive technical rehearsals and safety protocols should be implemented to familiarize performers with the digital elements and ensure smooth coordination between the choreography and motion graphics. This also includes establishing emergency procedures in the event of technical malfunctions or disruptions.
- Real-time Monitoring and Feedback: Incorporating motion graphics often requires real-time monitoring of digital elements to synchronize seamlessly with the live performance. Dedicated crew members should be responsible for monitoring visual effects and providing immediate feedback to performers to maintain a cohesive and safe performance environment.
- Post-performance Recovery: After each performance, performers and crew involved in incorporating motion graphics should undergo post-performance assessments to address any physical or mental strain resulting from the integration of technology into the dance performance.
The Impact of Technology on Dance
Beyond safety considerations, the integration of motion graphics in dance performances has a profound impact on the art form, offering new avenues for artistic exploration and audience engagement. By leveraging technology, dancers can extend their movements into digital realms, creating mesmerizing visual landscapes that transcend traditional stage boundaries. This immersive experience leaves a lasting impression on audiences and opens doors to interdisciplinary collaborations that redefine the possibilities of dance as a sensory art form.
Conclusion
As the realms of dance and technology converge, the incorporation of motion graphics in dance performances presents both exciting opportunities and critical safety considerations. By acknowledging the technical, artistic, and ergonomic aspects of this collaboration, performers and production teams can harness the power of technology to enrich the dance experience while prioritizing the safety and well-being of all involved. With careful planning and attention to safety protocols, the fusion of motion graphics and dance holds the potential to propel the art form into new frontiers.