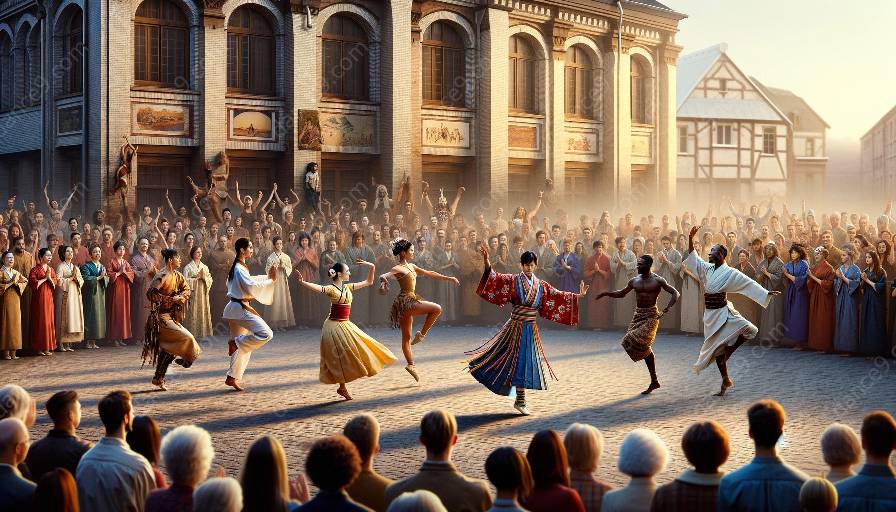
In the realm of cultural preservation and dance ethnography, understanding the impact of migration on the transmission of traditional dance forms is essential. As people move across borders and settle in new environments, they bring with them their cultural practices, including traditional dances. This phenomenon has both positive and negative implications for the preservation and evolution of traditional dance forms.
Migration and Cultural Preservation:
Migration plays a significant role in the preservation of traditional dance forms. When individuals or communities migrate, they carry their cultural heritage, including dance traditions, with them. This transfer of cultural knowledge helps preserve traditional dance forms by ensuring they are practiced and passed down to future generations. The diaspora communities formed through migration often become custodians of their cultural heritage, actively working to sustain and celebrate traditional dances in their new homelands.
On the other hand, migration can lead to the dilution or loss of traditional dance forms, particularly if migration disrupts the continuity of cultural transmission. Factors such as acculturation, assimilation, and the adoption of new dance styles in the host country can challenge the preservation of traditional dances. Therefore, it is crucial to examine how migration impacts the transmission of traditional dance forms to ensure their continued vitality and relevance within evolving cultural landscapes.
Migration and Dance Ethnography:
Dance ethnography, the study of dance within its cultural and social contexts, provides valuable insight into the ways in which migration influences the transmission of traditional dance forms. Ethnographers explore how migration shapes the performance, meaning, and function of traditional dances within diverse communities. By documenting the experiences of migrant dancers and the adaptation of traditional dances in new environments, dance ethnography contributes to a deeper understanding of cultural exchange and transformation.
Migrants often use dance as a means of connecting with their roots, expressing cultural identity, and fostering a sense of belonging in their adopted countries. This process of cultural negotiation through dance presents a rich area of study for dance ethnographers, highlighting the dynamic interplay between tradition and innovation in the context of migration. Through dance ethnography, researchers can elucidate the complex ways in which traditional dance forms evolve, endure, or disappear in response to migration and cultural encounters.
Migration and Cultural Studies:
From a cultural studies perspective, migration serves as a driving force behind the intercultural exchange of traditional dance forms. As migrants interact with diverse communities and engage in transnational cultural networks, traditional dances undergo adaptation, hybridization, and cross-pollination. This dynamic process of cultural fusion and reinvention reflects the changing nature of traditional dance forms in response to migration-related dynamics.
Cultural studies also consider the power dynamics and inequalities that impact the transmission of traditional dance forms in the context of migration. Economic, political, and social factors influence the visibility and accessibility of traditional dances in migrant communities, shaping the ways in which these art forms are valued and sustained. By critically analyzing the intersection of migration and traditional dance, cultural studies offer a holistic perspective on the complex relationships between mobility, identity, and cultural expression.
Conclusion:
Migration has a profound impact on the transmission of traditional dance forms, intersecting with the realms of cultural preservation, dance ethnography, and cultural studies. While migration can facilitate the preservation and revitalization of traditional dances by fostering diaspora communities and cultural exchange, it also presents challenges that may threaten the authenticity and continuity of these art forms. Understanding the multi-faceted influence of migration on traditional dance forms is essential for safeguarding cultural heritage, fostering intercultural dialogue, and promoting the diverse expressions of human creativity through dance.