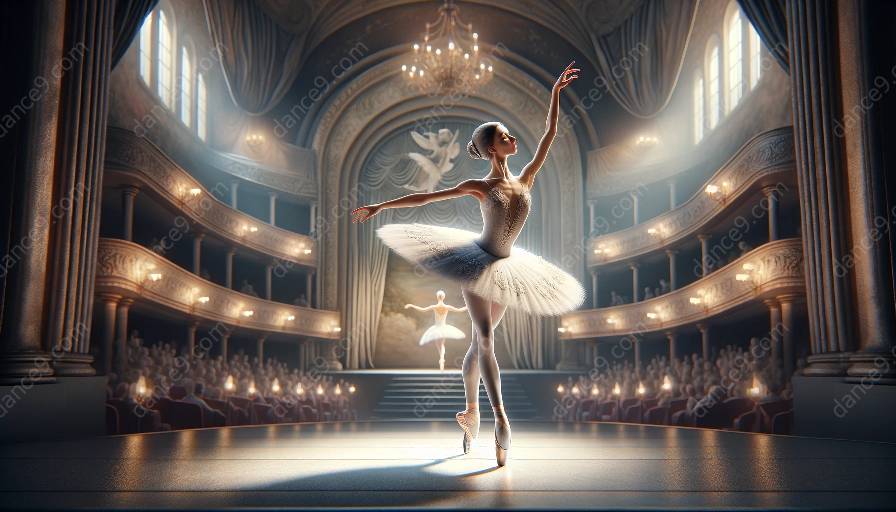
Ballet choreography principles form the foundational framework that shapes the elegant and harmonious movements seen in ballet and are essential for dance classes. Understanding these principles enhances the essence of ballet and brings out the artistry of the dancers.
Introduction to Ballet Choreography Principles
Ballet is a highly expressive and graceful form of dance that requires tremendous skill and dedication. Ballet choreography principles guide the composition and coordination of movements to create visually stunning and emotionally captivating performances. These principles are rooted in tradition and have evolved over centuries to reflect the art form's expressive and technical aspects.
1. Alignment and Posture
One of the fundamental principles of ballet choreography is the emphasis on proper alignment and posture. Dancers must maintain a straight and elongated spine, aligned shoulders, and engaged core to achieve the characteristic grace and poise associated with ballet. Correct alignment not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the movements but also prevents injuries.
Elements of Alignment and Posture
- Alignment of the spine and limbs
- Placement of the head and neck
- Maintenance of a strong and centered core
2. Musicality and Timing
Ballet choreography is intricately intertwined with music, and dancers must embody the spirit of the music through their movements. Understanding musicality and timing is crucial for interpreting the rhythm and emotions within the music, thus creating a harmonious fusion of dance and music.
Key Aspects of Musicality
- Phrasing and dynamics
- Syncopation and accents
- Interpretation of different musical styles
3. Fluidity and Linearity
Ballet movements are characterized by their inherent fluidity and linearity. Dancers strive to create seamless transitions between poses and movements, emphasizing the continuity and grace inherent in ballet. The pursuit of exquisite lines and extensions is a hallmark of ballet choreography.
Techniques for Fluidity and Linearity
- Emphasis on smooth transitions
- Focused extension and elongation of limbs
- Maintaining a sense of flow in movements
4. Symmetry and Opposition
Ballet choreography often explores the concept of symmetry and opposition, where movements are balanced and counterbalanced to create visually appealing and harmonious compositions. This principle guides the spatial dynamics and interactions between dancers, enhancing the overall aesthetic of the performance.
Utilizing Symmetry and Opposition
- Creating visually balanced formations
- Exploring mirroring and counter-movements
- Enhancing spatial relationships between dancers
5. Storytelling and Expression
Ballet is a powerful storytelling medium, and choreography plays a pivotal role in conveying narratives and emotions. Through expressive movements and gestures, ballet choreography brings stories and emotions to life, captivating audiences and evoking profound emotional responses.
Narrative Elements in Ballet Choreography
- Use of gestures and mime to convey emotions
- Depiction of character dynamics and interactions
- Emotional resonance through movement and expression
Conclusion
Ballet choreography principles are the guiding force behind the mesmerizing beauty and emotional depth of ballet performances. Understanding these principles not only enriches the experience of ballet but also serves as a foundational framework for dancers in various dance classes. By delving into the intricacies of alignment, musicality, fluidity, symmetry, and storytelling, dancers can elevate their artistry and bring forth the true essence of ballet.